contain multitudes • por Padma Dorje • fundado em 2003
contain multitudes
 pdf
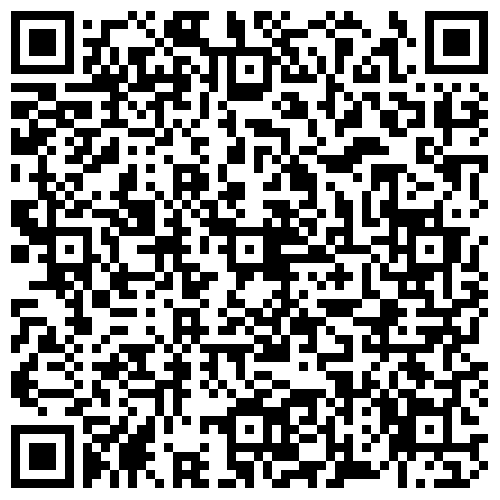
pdfVon Neumann's First Computer Program
An analysis of the two earliest sets of instruction codes planned for stored program computers, and the earliest extant program for such a computer, gives insight into the thoughts of John yon Neumann, the man who designed the instruction sets and wrote the program, and shows how several important aspects of computing have evolved. The paper is based on previously unpubhshed documents from the files of Herman H. Goldstine.
 PDF
PDFWhy Philosophers Should Care About Computational Complexity
One might think that, once we know something is computable, how efficiently it can be computed is a practical question with little further philosophical importance. In this essay, I offer a detailed case that one would be wrong. In particular, I argue that computational complexity theory—the field that studies the resources (such as time, space, and randomness) needed to solve computational problems—leads to new perspectives on the nature of mathematical knowledge, the strong AI debate, computationalism, the problem of logical omniscience, Hume’s problem of induction, Goodman’s grue riddle, the foundations of quantum mechanics, economic rationality, closed timelike curves, and several other topics of philosophical interest. I end by discussing aspects of complexity theory itself that could benefit from philosophical analysis.
 YouTube
YouTubeComputing Limit
Just how far can we go with processing speed? Physicist Professor Phil Moriarty talks about the hard limits of computing.
 Arxiv
ArxivMarkets are efficient if and only if P = NP
I prove that if markets are weak-form efficient, meaning current prices fully reflect all information available in past prices, then P = NP, meaning every computational problem whose solution can be verified in polynomial time can also be solved in polynomial time. I also prove the converse by showing how we can "program" the market to solve NP-complete problems. Since P probably does not equal NP, markets are probably not efficient. Specifically, markets become increasingly inefficient as the time series lengthens or becomes more frequent. An illustration by way of partitioning the excess returns to momentum strategies based on data availability confirms this prediction.
 Wikipedia
WikipediaLogic Theorist
Logic Theorist is a computer program written in 1955 and 1956 by Allen Newell, Herbert A. Simon and Cliff Shaw. It was the first program deliberately engineered to mimic the problem solving skills of a human being and is called "the first artificial intelligence program". It would eventually prove 38 of the first 52 theorems in Whitehead and Russell's Principia Mathematica, and find new and more elegant proofs for some.
 duartes
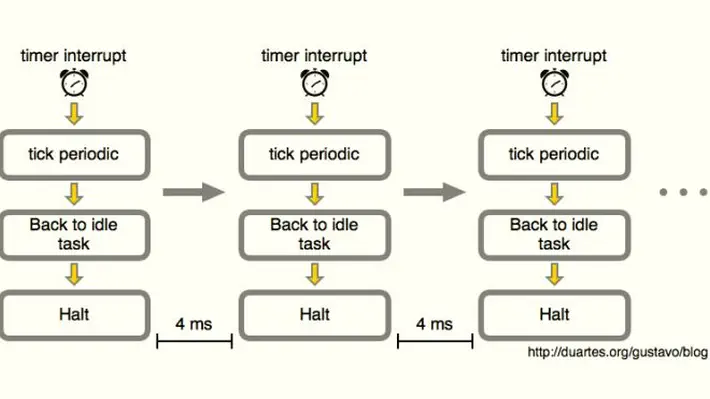
duartesWhat Does an Idle CPU Do?
In the last post I said the fundamental axiom of OS behavior is that at any given time, exactly one and only one task is active on a CPU. But if there’s absolutely nothing to do, then what?
 COMPUTERS-ARE-FAST
COMPUTERS-ARE-FASTOne second code
Do YOU know how much your computer can do in a second? // Let's find out how well you know computers! All of these programs have a variable NUMBER in them. Your mission: guess how big NUMBER needs to get before the program takes 1 second to run.
 GWERN
GWERNEssays by Gwern Branwen
Researcher, self-experimenter, and writer: psychology, statistics, and technology. Categorized list of gwern.net pages.
 CLERRO
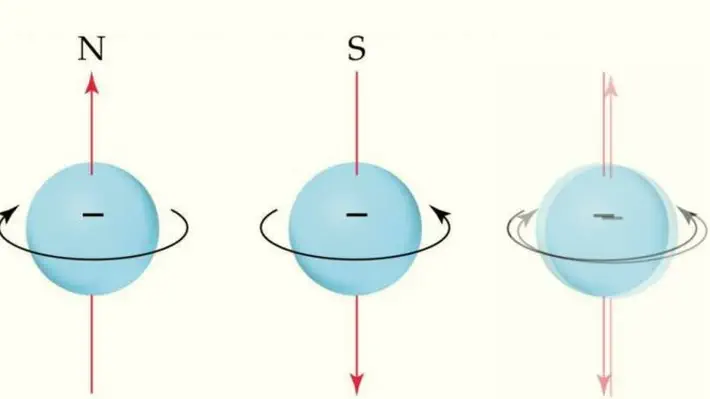
CLERROQuantum Computing Explained
Weird phenomena like Quantum Tunnelling take such prominence, that they can't be ignored. One way to solve this issue, could be to find a new way to use these principles of quantum mechanics to perform computations, in a way using it to our advantage. This pushes us to think seriously about quantum computing.
 AEON
AEON pdf
pdf nature
nature PDF
PDF YouTube
YouTube Arxiv
Arxiv Wikipedia
Wikipedia Linux Voice
Linux Voice duartes
duartes quantamagazine
quantamagazine COMPUTERS-ARE-FAST
COMPUTERS-ARE-FAST GWERN
GWERN CLERRO
CLERRO EXTREMETECH
EXTREMETECH plus
plus






